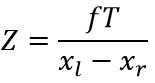Ondrej Galbavy
This example presents straightforward process to determine depth of points (sparse depth map) from stereo image pair using stereo reconstruction. Example is implemented in Python 2.
Stereo calibration process
We need to obtain multiple stereo pairs with chessboard shown on both images.

- For each stereo pair we need to do:
- Find chessboard: cv2.findChessboardCorners
- Find subpixel coordinates: cv2.cornerSubPix
- If both chessboards are found, store keypoints
- Optionally draw chessboard pattern on image
- Compute calibraton: cv2.stereoCalibrate
- We get:
- Camera matrices and distortion coefficients
- Rotation matrix
- Translation vector
- Essential and fundamental matrices
- We get:
- Store calibration data for used camera setup
for paths in calib_files: left_img = cv2.imread(paths.left_path, cv2.CV_8UC1) right_img = cv2.imread(paths.right_path, cv2.CV_8UC1) image_size = left_img.shape find_chessboard_flags = cv2.CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | cv2.CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE | cv2.CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK left_found, left_corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(left_img, pattern_size, flags = find_chessboard_flags) right_found, right_corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(right_img, pattern_size, flags = find_chessboard_flags) if left_found: cv2.cornerSubPix(left_img, left_corners, (11,11), (-1,-1), (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.1)) if right_found: cv2.cornerSubPix(right_img, right_corners, (11,11), (-1,-1), (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.1)) if left_found and right_found: img_left_points.append(left_corners) img_right_points.append(right_corners) obj_points.append(pattern_points) cv2.imshow("left", left_img) cv2.drawChessboardCorners(left_img, pattern_size, left_corners, left_found) cv2.drawChessboardCorners(right_img, pattern_size, right_corners, right_found) cv2.imshow("left chess", left_img) cv2.imshow("right chess", right_img) stereocalib_criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 100, 1e-5) stereocalib_flags = cv2.CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO | cv2.CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST | cv2.CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH | cv2.CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL | cv2.CALIB_FIX_K3 | cv2.CALIB_FIX_K4 | cv2.CALIB_FIX_K5 stereocalib_retval, cameraMatrix1, distCoeffs1, cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2, R, T, E, F = cv2.stereoCalibrate(obj_points,img_left_points,img_right_points,image_size,criteria = stereocalib_criteria, flags = stereocalib_flags)
Stereo rectification process
We need to:
- Compute rectification matrices: cv2.stereoRectify
- Prepare undistortion maps for both cameras: cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap
- Remap each image: cv2.remap
rectify_scale = 0 # 0=full crop, 1=no crop
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, roi1, roi2 = cv2.stereoRectify(data["cameraMatrix1"], data["distCoeffs1"], data["cameraMatrix2"], data["distCoeffs2"], (640, 480), data["R"], data["T"], alpha = rectify_scale)
left_maps = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(data["cameraMatrix1"], data["distCoeffs1"], R1, P1, (640, 480), cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_maps = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(data["cameraMatrix2"], data["distCoeffs2"], R2, P2, (640, 480), cv2.CV_16SC2)
for pair in pairs:
left_img_remap = cv2.remap(pair.left_img, left_maps[0], left_maps[1], cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
right_img_remap = cv2.remap(pair.right_img, right_maps[0], right_maps[1], cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
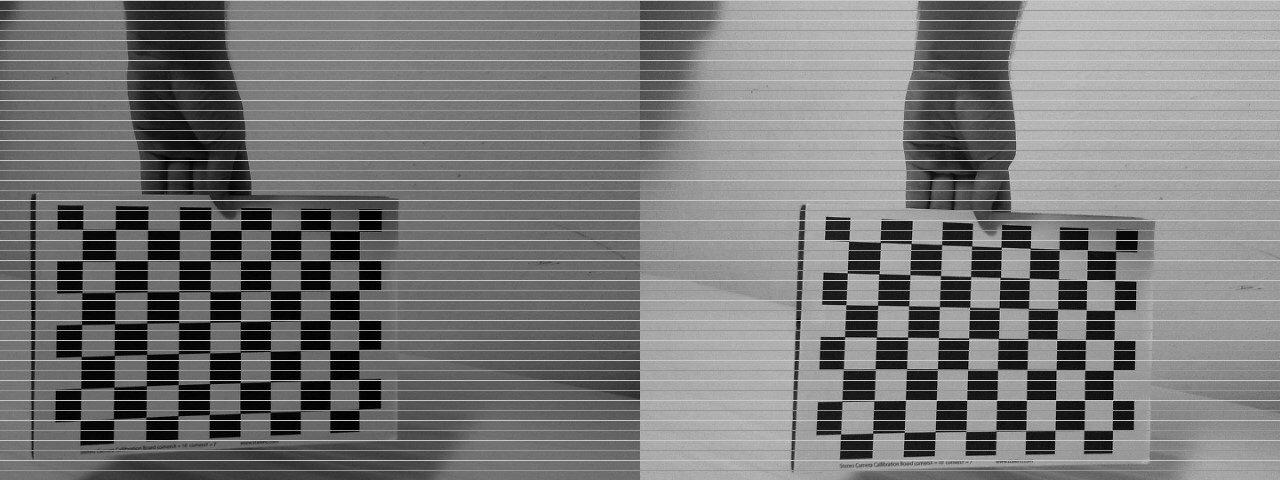
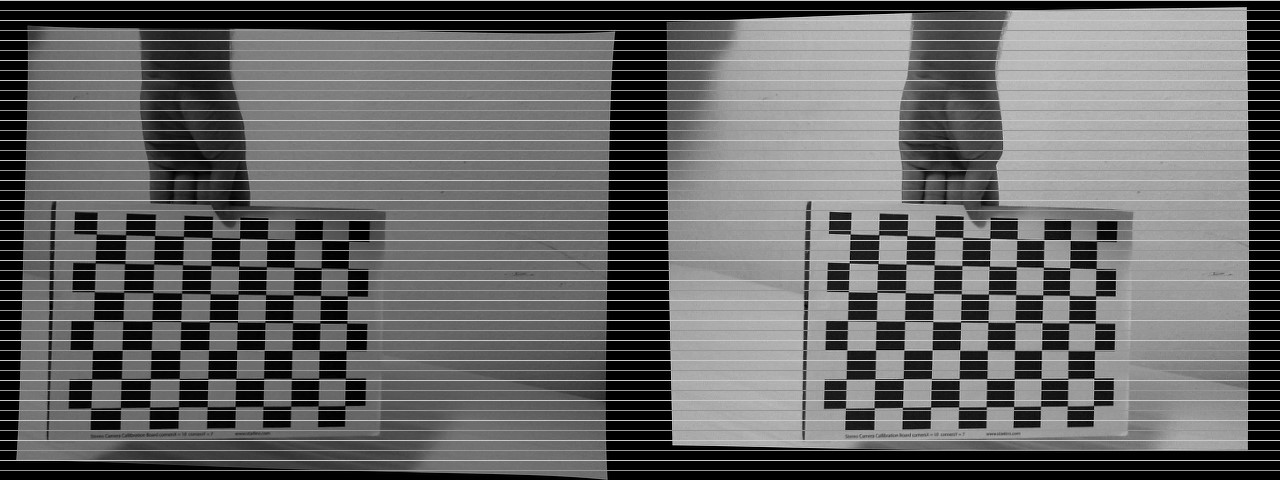
Stereo pairing
Standard object matching: keypoint detection (Harris, SIFT, SURF,…), descriptor extractor (SIFT, SURF) and matching (Flann, brute force,…). Matches are filtered for same line coordinates to remove mismatches.
detector = cv2.FeatureDetector_create("HARRIS")
extractor = cv2.DescriptorExtractor_create("SIFT")
matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create("BruteForce")
for pair in pairs:
left_kp = detector.detect(pair.left_img_remap)
right_kp = detector.detect(pair.right_img_remap)
l_kp, l_d = extractor.compute(left_img_remap, left_kp)
r_kp, r_d = extractor.compute(right_img_remap, right_kp)
matches = matcher.match(l_d, r_d)
sel_matches = [m for m in matches if abs(l_kp[m.queryIdx].pt[1] - r_kp[m.trainIdx].pt[1]) < 3]


Triangulation
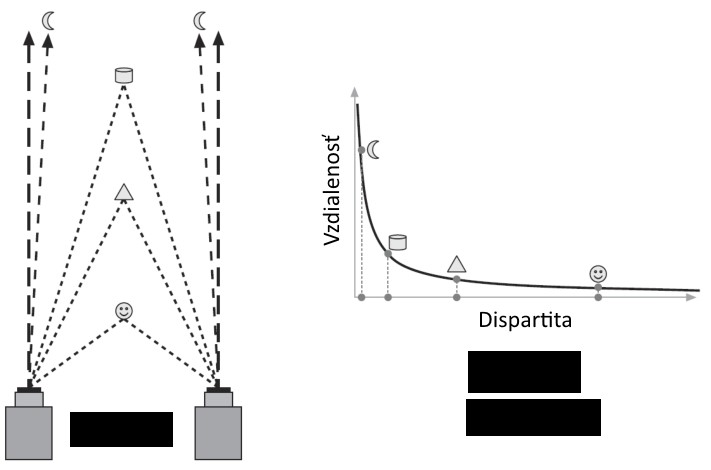
How do we get depth of point? Dispartity is difference of x coordinate of the same keypoint in both images. Closer points have greater dispartity and far points have almost zero dispartity. Depth can be defined as:
Where:
- f – focal length
- T – baseline – distance of cameras
- x1, x2 – x coordinated of same keypoint
- Z – depth of point
for m in sel_matches:
left_pt = l_kp[m.queryIdx].pt
right_pt = r_kp[m.trainIdx].pt
dispartity = abs(left_pt[0] - right_pt[0])
z = triangulation_constant / dispartity
Result